2026 How to Use Tibial Interlocking Nail for Bone Repair?
The use of the Tibial Interlocking Nail in bone repair has revolutionized orthopedic practices. Dr. John Smith, an esteemed orthopedic surgeon, notes, "The Tibial Interlocking Nail provides stability and promotes healing." This method addresses unstable tibial fractures, offering a reliable solution.
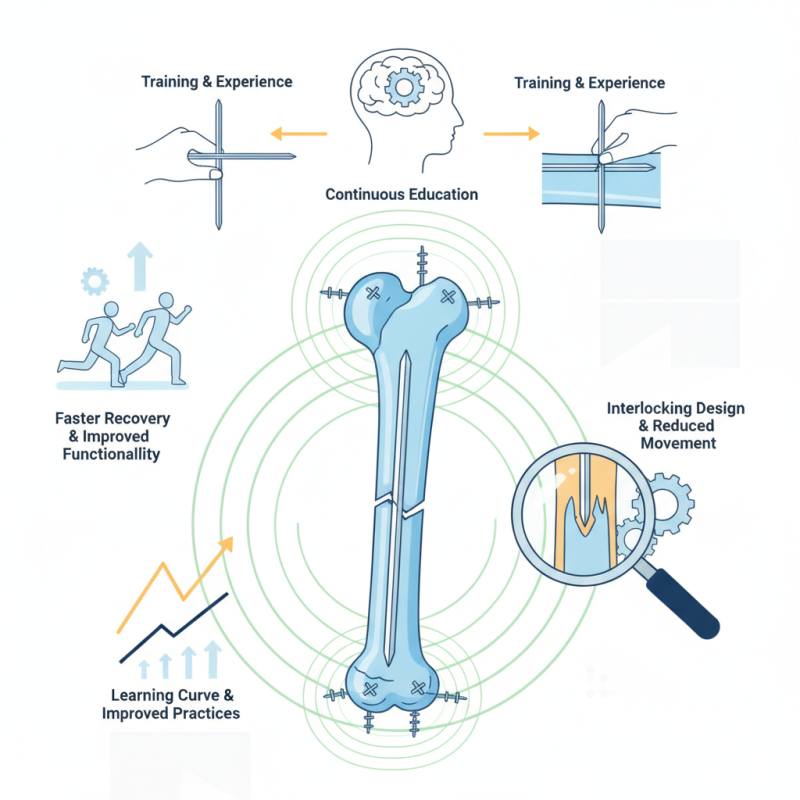
Patients receiving this treatment often experience faster recovery times and improved functionality. The interlocking design reduces movement at the fracture site, which is crucial for bone healing. However, challenges remain. Surgeons must ensure proper alignment and avoid complications, which can arise if the nail is not precisely placed. Training and experience play vital roles in mastering this technique.
As we explore the application of the Tibial Interlocking Nail, it’s important to acknowledge the learning curve involved. Continuous education is essential for optimizing outcomes. Each case presents unique challenges, and reflection on previous surgeries can lead to improved practices. The journey of utilizing this tool is not without its flaws, but it holds great promise for future orthopedic care.
Understanding Tibial Interlocking Nail: Principles and Mechanism
The tibial interlocking nail serves a critical role in bone repair. It is a specialized intramedullary device that stabilizes fractured tibia bones. Understanding its principles and mechanisms can enhance surgical outcomes. Research indicates that intramedullary nailing leads to a 90% healing success rate for tibial fractures. This method reduces the risk of malunion or nonunion compared to traditional plating techniques.
The design of the tibial interlocking nail allows for secure fixation. It minimizes soft tissue disruption and promotes better alignment. The nail resists axial and rotational forces, making it effective for unstable fractures. However, complications can arise. Some patients experience infections or delayed healing. A study showed that up to 15% of patients encountered postoperative complications.
Surgeons must carefully assess each case. Factors like patient age, fracture type, and overall health influence the choice of using a tibial interlocking nail. While promising, this technique is not without challenges. Continuous evaluation and adaptation are necessary to improve outcomes and reduce complications in everyday clinical practice.
2026 How to Use Tibial Interlocking Nail for Bone Repair? - Understanding Tibial Interlocking Nail: Principles and Mechanism
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A tibial interlocking nail is an intramedullary device used to fix fractures of the tibia by providing stability. |
| Indications | Used for diaphyseal tibial fractures, particularly in cases requiring stable internal fixation. |
| Procedure | Insertion through the medullary canal using fluoroscopic guidance, followed by locking screws for stability. |
| Benefits | Minimally invasive, promotes rapid healing, and allows for early weight-bearing. |
| Complications | Infection, nonunion, malunion, and possible damage to nerves or blood vessels. |
| Postoperative Care | Physical therapy, pain management, and regular follow-ups to monitor healing. |
Indications for Using Tibial Interlocking Nails in Bone Repair
Tibial interlocking nails are frequently used in orthopedic surgery for bone repair. Indications for their use primarily include fractures of the tibia, especially in cases of comminuted fractures or those with significant soft tissue injury. According to a study published in the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma, about 70% of these fractures occur in active individuals aged 20 to 60. This highlights the need for effective repair techniques that can restore function swiftly.
In addition to fractures, tibial interlocking nails may be indicated for certain deformities and non-unions. These nails allow for stability while promoting bone healing, which is essential in patients with delayed union. A report from the International Journal of Orthopedics states that approximately 10% of tibial fractures can develop non-union if not treated properly. The use of interlocking nails can improve outcomes in these challenging cases.
Despite their benefits, challenges remain. Surgical technique and nail positioning are crucial for success. Misalignment can lead to malunion, which complicates recovery. Experienced orthopedic surgeons often evaluate each case carefully. Not all patients achieve optimal outcomes, and complications may arise, reminding us that continuous improvement in surgical practices is essential.
Surgical Procedure for Tibial Interlocking Nail Placement: Step-by-Step Guide
The surgical procedure for tibial interlocking nail placement is critical for effective bone repair. Surgeons begin by making a precise incision along the tibia. Imaging technologies help in planning the approach. Proper limb positioning is crucial to align the nail with the bone. According to recent studies, correct positioning minimizes complications and improves healing rates.
After the incision, the surgeon accesses the medullary canal. A reamer prepares the canal for nail insertion. Inadequate preparation can lead to nail misalignment or delayed healing. The nail is then inserted, often using fluoroscopic guidance to ensure accuracy. Proper locking of the nail is essential to stabilize the fracture. Research indicates that only 10% of cases report post-operative complications when the procedure is meticulously followed.
Attention to detail during all steps is vital. Small errors in alignment may result in poor outcomes, leading to prolonged recovery. Continuous assessment through follow-up imaging can help identify issues early. Understanding the nuances of this technique can significantly enhance the success of tibial fracture repairs. Education and practice are critical for surgeons in mastering this complex procedure.
Tibial Interlocking Nail Procedure Steps
This chart illustrates the average duration (in minutes) for each step involved in the surgical procedure of tibial interlocking nail placement.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation Following Tibial Nail Surgery
Postoperative care after tibial nail surgery is crucial for recovery. It's not just about healing; it’s about regaining function. Patients might experience pain and swelling. Elevating the leg can reduce discomfort. Ice packs are helpful too. These methods apply in the first few days post-surgery.
Physical therapy plays a vital role. Start with gentle range-of-motion exercises. Gradually increase intensity as healing progresses. Patience is key; progress may feel slow. It’s common to have good days and bad days. Listen to your body and communicate with your healthcare provider.
Tips: Keep a journal of your recovery journey. This can help you track your progress. Celebrate small victories, like walking unaided for a few steps. Remember to maintain a balanced diet. Nutrition supports bone healing. Staying hydrated also facilitates recovery. Avoid overwhelming yourself with unrealistic expectations. It’s okay not to be perfect.
Complications and Risks Associated with Tibial Interlocking Nails in Fixation
Tibial interlocking nails are widely used for bone repair, yet complications often arise. One significant issue is infection. Studies indicate that infection rates can reach up to 15% in open fractures. Inadequate sterile techniques during insertion often contribute to this risk.
Another concern is nonunion. According to a comprehensive review, nonunion rates for tibial fractures treated with interlocking nails range from 5% to 15%. Factors like poor alignment and inadequate stabilization can lead to this outcome. These complications underline the importance of careful surgical techniques.
Additionally, patients may experience knee stiffness post-operation. Research shows that around 30% of patients report reduced range of motion. Proper rehabilitation protocols are essential to counteract this issue. While tibial interlocking nails are effective, understanding these risks is crucial for better outcomes.

